Table of Contents
What is Water Tube Boiler
A watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates through tubes that are heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum.
Watertube boilers are typically larger and can handle higher pressure and temperatures than firetube boilers. They also have a higher thermal efficiency, which means they can convert a larger amount of fuel into useful energy. Watertube boilers are used in thermal power plant, industrial facilities, and ships.
Water tube boilers are a type of boiler that uses water circulating through a network of tubes to generate steam or hot water. The water is heated by combustion gases that flow around the tubes, in contrast to fire tube boilers, where the water surrounds the hot gases. Water tube boilers are more efficient, faster, and can handle higher pressures than fire tube boilers. They are commonly used in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and petrochemicals.
 Water tube Boiler
Water tube Boiler
Water tube boilers are commonly used in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and petrochemicals, where high-pressure steam is required for various processes.
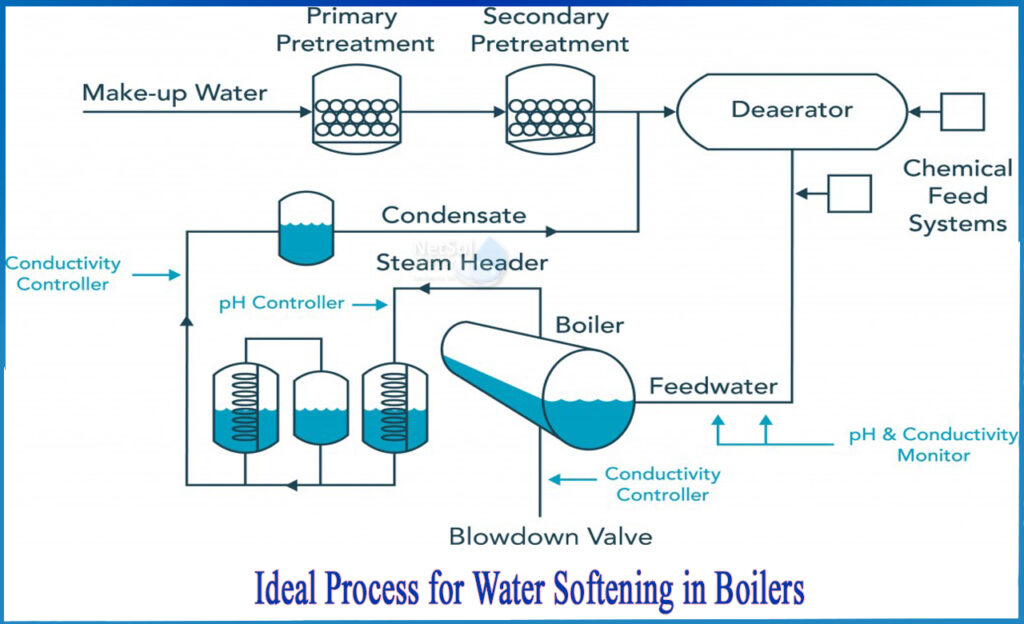
The construction of a water tube boiler typically involves a steam drum at the top, where water and steam are separated. Water enters the boiler from the bottom and is heated as it flows through the tubes. The heated water rises and collects in the steam drum, where steam is separated and can be drawn off for various applications. The remaining water, which hasn’t turned into steam, continues its journey through the tubes, getting reheated and eventually reaching the steam drum.
Water tube boilers are a versatile and efficient solution for industrial steam and hot water generation. They are capable of handling high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
HOW A WATERTUBE BOILER WORKS
Water tube boilers are commonly used for high-pressure applications, such as in power plants and industrial processes. These boilers differ from traditional fire-tube boilers, where hot gases from the combustion process flow through tubes carrying water. In water tube boilers, water flows through the tubes while hot combustion gases flow over them. Here’s how they work:
- Water is pumped into the boiler from an external source, such as a tank or a water treatment system.
- The water flows through a series of tubes, which form the walls of the boiler’s furnace. Fuel, such as natural gas, coal, or oil, is burned, and the resulting hot gases flow over the tubes.
- Heat from the combustion gases is transferred to the water inside the tubes, causing it to heat up and generate steam.
- The steam rises to the top of the boiler and is collected in a steam drum, where it is separated from any remaining water.
- The dry steam is then piped out of the drum and used for energy generation or other processes.
Water tube boilers offer several advantages over fire-tube boilers, including higher efficiency, faster steam generation, and the ability to handle higher pressures and temperatures. However, they are typically more complex and expensive to manufacture and maintain.
Water Tube Boiler Working Principle
- Fuel combustion: The first step is to burn fuel in the furnace. The fuel can be any type of combustible material, such as coal, oil, or natural gas. The combustion process creates hot gases, which are the source of heat for the boiler.
- Water heating: The hot gases from the furnace flow through the water tubes, heating the water inside the tubes. The water tubes are made of a material that can withstand high temperatures, such as steel or copper. The water is heated until it reaches the boiling point, at which point it turns into steam.
- Steam separation: The steam rises to the steam drum, where it is separated from the water. The steam drum is a large vessel that is located at the top of the boiler. The steam is drawn off from the steam drum for use in various applications.
- Water circulation: The remaining water flows back down to the furnace, where it is reheated and the process repeats. The water circulation process is driven by the difference in density between hot water and cold water. Hot water is less dense than cold water, so it rises to the top of the boiler. This creates a circulation loop, with the hot water rising to the top and the cold water flowing down to the bottom.
Water tube boilers are a very efficient way to generate steam or hot water. They are also capable of handling high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
ADVANTAGES OF WATERTUBE BOILER
Water tube boilers offer a range of advantages over other types of boilers, making them a preferred choice for various applications. Their key benefits include:
Enhanced Efficiency: Water tube boilers boast superior efficiency in converting fuel into usable energy. The direct contact between the combustion gases and the tubes minimises heat loss, maximising the energy extracted from the fuel.
Boosted Safety: Water tube boilers are designed with safety in mind. The water-filled tubes efficiently dissipate heat, preventing overheating and reducing the risk of explosions or other safety hazards.
Rapid Steam Generation: Water tube boilers are engineered to generate steam quickly. The rapid movement of water within the tubes expedites heat transfer, leading to faster steam production compared to firetube boilers.
Reduced Sediment Deposition: Water tube boilers typically experience less sediment buildup than firetube boilers. The high-pressure steam flow within the tubes helps prevent sediment accumulation, minimising maintenance requirements and enhancing overall efficiency.
Versatility and Adaptability: Water tube boilers can be tailored to a wide range of applications, accommodating various fuel sources and operating pressures. They can be customised to meet specific steam production requirements, making them versatile solutions for diverse industrial and commercial needs.
Long-Term Reliability: Water tube boilers are known for their durability and longevity. Their robust construction and well-designed components ensure a long lifespan, minimising downtime and maximising return on investment
Industries that commonly use watertube boilers
Industries commonly using watertube boilers include:
- Power Generation: Watertube boilers are widely utilised in power plants to generate steam for electricity production. They are favoured due to their capability to handle high pressures and temperatures.
- Petrochemical Industry: Watertube boilers are prevalent in the petrochemical industry for steam generation used in various processes like heat exchangers, distillation, and chemical reactions.
- Refining Industry: Watertube boilers are vital in the refining industry for processes such as distillation, cracking, and hydrogen production.
- Food Processing Industry: Watertube boilers are employed in the food processing industry for applications such as cooking, sterilisation, and drying.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: The pharmaceutical manufacturing sector uses watertube boilers for processes like sterilisation, drying, and equipment cleaning.
- Paper and Pulp Industry: In the paper and pulp industry, watertube boilers are used for processes like drying and bleaching.
- Textile Industry: Watertube boilers are utilised for dyeing, drying, and fabric finishing in the textile industry.
- Chemical Industry: Watertube boilers are commonly used in the chemical industry for processes involving chemical reactions, heat exchange, and solvent recovery.
Types of water tube boilers
There are many different types of water tube boilers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of water tube boilers include:
- Drum boilers: Drum boilers are the most common type of water tube boiler. They have a large steam drum at the top, where water and steam are separated. Drum boilers are typically used for applications that require a large amount of steam
 Drum Water Tube Boiler
Drum Water Tube Boiler
- Once-through boilers: Once-through boilers are designed to generate steam as quickly as possible. They do not have a steam drum, and the water is heated directly in the tubes. Once-through boilers are typically used for applications that require a large amount of steam on demand, such as power generation
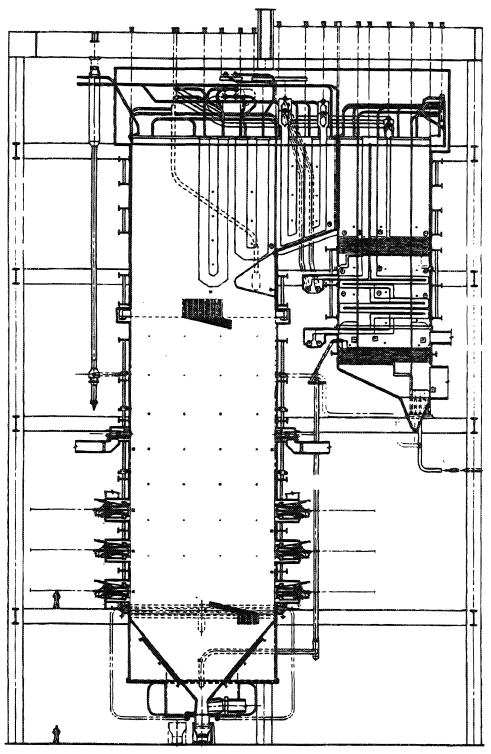
- Vertical boilers: Vertical boilers are typically used for smaller applications, such as heating buildings or providing steam for industrial processes. They are more compact than horizontal boilers, and they can be mounted on a wall or the ground.
- Horizontal boilers: Horizontal boilers are typically used for larger applications, such as power generation or industrial processing. They are more efficient than vertical boilers, but they are also more expensive.
Horizontal Water Tube Boiler
- Package boilers: Package boilers are pre-assembled boilers that are delivered to the site and ready to be installed. Package boilers are a good option for applications where space is limited or where the boiler needs to be installed quickly.
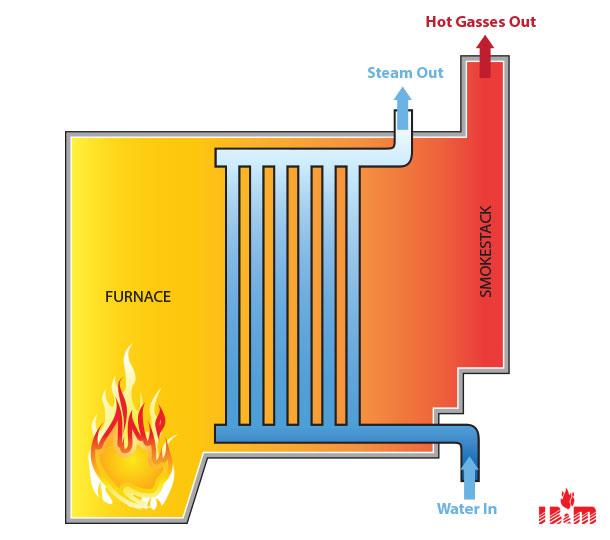
- Superheaters: Superheaters are boilers that are designed to produce steam at very high temperatures. Superheaters are typically used in power plants where high temperature steam is required.
 Super heater Water Tube Boiler
Super heater Water Tube Boiler
- Regenerative boilers: Regenerative boilers are boilers that use the heat from the flue gases to preheat the combustion air. This reduces the amount of fuel that is required to heat the water, which makes regenerative boilers more efficient then conventional boiler.
The type of water tube boiler that is best for a particular application will depend on a number of factors, including the amount of steam that is required, the pressure and temperature of the steam, and the space that is available.
Parts and Functions of a Water tube boiler
- Furnace: The furnace is where the fuel is burned to create heat. The heat from the furnace is transferred to the water in the tubes.
- Water tubes: The water tubes are the channels through which the water flows. The water is heated by the hot gases that flow around the tubes.
- Steam drum: The steam drum is a large vessel at the top of the boiler where water and steam are separated. The steam is drawn off from the steam drum for use in various applications.
- Circulation system: The circulation system is responsible for circulating the water through the tubes. The circulation system can be natural circulation or forced circulation. In natural circulation, the water is circulated by the difference in density between hot water and cold water. In forced circulation, the water is circulated by pumps.
- Safety valves: Safety valves are valves that open to release steam if the pressure gets too high. This prevents the boiler from exploding.
- Water level indicator: The water level indicator is a device that shows the water level in the boiler. This is important to ensure that the boiler does not run out of water.
Water Tube Boiler FAQ
A water tube boiler is a type of boiler in which the water is circulated through tubes that are surrounded by hot gases from the combustion of fuel. This allows for more efficient heat transfer than other types of boilers, such as fire tube boilers.
Water tube boilers have several advantages over other types of boilers, including:
Higher efficiency: Water tube boilers are more efficient at transferring heat from the fuel to the water, which can save energy costs.
Larger capacity: Water tube boilers can be made larger than other types of boilers, which makes them suitable for industrial applications that require a lot of steam.
Higher operating pressure: Water tube boilers can operate at higher pressures than other types of boilers, which makes them suitable for generating high-pressure steam.
More compact design: Water tube boilers can be designed to be more compact than other types of boilers, which can save space.
Water tube boilers also have some disadvantages, including:
More complex design: Water tube boilers are more complex to design and manufacture than other types of boilers.
More expensive: Water tube boilers are more expensive than other types of boilers.
More difficult to maintain: Water tube boilers are more difficult to maintain than other types of boilers.
There are many different types of water tube boilers, but some of the most common types include:
Horizontal water tube boilers: These boilers have the water tubes arranged horizontally.
Vertical water tube boilers: These boilers have the water tubes arranged vertically.
Once-through water tube boilers: These boilers use a single pass of water through the tubes, which makes them very efficient.
Multi-pass water tube boilers: These boilers use multiple passes of water through the tubes, which can improve efficiency.
Packaged water tube boilers: These boilers are pre-assembled and skid-mounted, which makes them easy to install.
The main parts of a water tube boiler include:
Furnace: The furnace is where the fuel is burned to heat the water.
Water tubes: The water tubes are the tubes through which the water flows.
Steam drum: The steam drum is where the steam is generated.
Feedwater pump: The feedwater pump is used to circulate the water through the tubes.
Safety valves: The safety valves are used to relieve excess pressure in the boiler.
Other components: Other components of a water tube boiler may include a control system, a blowdown system, and a water treatment system.
The working principle of a water tube boiler is as follows:
Fuel is burned in the furnace, which heats up the water in the water tubes.
The hot water rises to the steam drum, where it turns into steam.
The steam is then released from the steam drum and used for heating or power generation.
What is the application of water tube boilers?
Power plants
Industrial plants
Commercial buildings
Residential buildings
Ships
Railroads
Other applications that require steam
Water tube boilers require regular maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operation. Some of the key maintenance tasks include:
Cleaning the water tubes to remove scale and other deposits.
Testing and inspecting the safety valves.
Treating the water to prevent corrosion and scale buildup.
Replacing worn or damaged parts.
Water tube boilers can pose a number of safety hazards, including:
Explosion: If the pressure in the boiler gets too high, it can explode.
Fire: The fuel in the furnace can ignite, causing a fire.
Scalding: Hot steam can cause scalding burns.
Corrosion: The water in the boiler can corrode the metal parts, leading to leaks and other problems.
To prevent water tube boiler accidents, it is important to:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for operation and maintenance.
Conduct regular inspections and maintenance.
Train operators on safe operating procedures.
Install and use safety devices, such as pressure relief valves and flame detectors.
 Water tube Boiler
Water tube Boiler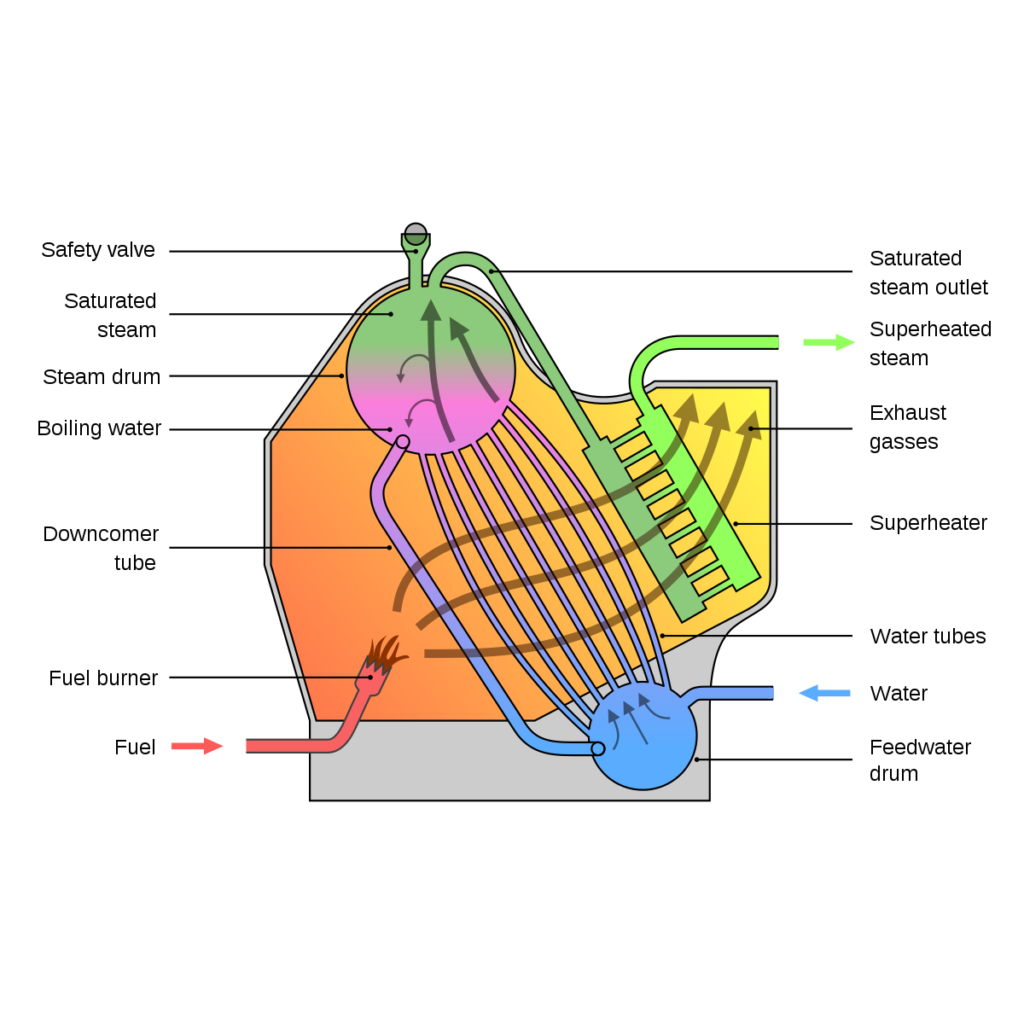 Drum Water Tube Boiler
Drum Water Tube Boiler