Table of Contents
What is a Boiler? How Boosting Production Efficiency
A boiler is a closed vessel in which water is heated to produce steam or hot water. The steam or hot water is then used for a variety of purposes, including heating buildings, generating electricity, and sterilizing equipment.
Boilers convert water into steam or hot water, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including heating, steam production, and power generation. They are available in a range of designs to meet the specific needs of different industries.
Thermodyne boilers offer several advantages, including:
- Reliable and efficient: Thermodyne boilers are designed to operate for extended periods without breakdowns, ensuring a consistent supply of thermal energy. They are also highly efficient, using fuel resources effectively.
- Versatility: Thermodyne boilers come in a variety of configurations to suit different industrial applications. They are available as fire-tube, water-tube, and electric boilers, catering to diverse fuel sources and operational requirements.
- Control: Thermodyne boilers provide precise control over steam temperature and pressure, ensuring optimal performance in various industrial processes. This is essential for applications like sterilization, power generation, and heating systems.
By utilizing Thermodyne boilers, industries can enhance their production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and achieve their manufacturing goals. Their reliable performance, versatility, and control capabilities make them a valuable asset in today’s industrial landscape.
The basic principle of a boiler is to convert water into steam with heat energy. This is done by burning fuel in a furnace, which produces hot gasses. These gasses are then passed through a heat exchanger, where they transfer their heat to the water. The water is heated until it reaches its boiling point and vaporizes into steam.
Boilers are a type of heating equipment that use heat to produce steam. The steam is then used to generate power, heat water, or provide a source of hot air. Boilers are used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and foodservice.
In this post, we will provide an expert guide to boilers, covering everything you need to know about their definition, components, applications, and functions. We will also discuss the importance of boiler safety and how to properly maintain and inspect your boiler.
Whether you are a new boiler owner or you are simply looking for more information about boilers, this post is for you. We hope you find it helpful!
Definition of Boilers

Boilers are defined as
“Boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other liquid is heated, steam or vapor is generated, steam is super-heated, or any combination thereof, under pressure or vacuum, for use external to itself, by the direct application of energy from the combustion of fuels, from electricity or nuclear energy. “
The boiler is a primary part of global heating system in power plants. ”
- The boiler system functions with the heat distribution system, heat-emitting system & control systems.
- Boiler is the main working component of thermal power plants
An industrial boiler is a closed vessel system that plays a vital role in various applications. It can withstand incredibly high pressures, far beyond what a pressure cooker can handle, making it an essential component in industries worldwide.
Boilers serve two primary functions: producing hot water and generating steam. Hot water boilers are used for domestic and commercial heating and hot water supply, while steam boilers are designed to create steam for a range of applications, including powering turbines for electricity generation and industrial heating processes.
When a boiler generates steam, it harnesses a significant amount of energy. Think of this steam as the driving force that powers a turbine. As the steam passes through the turbine’s blades, it imparts force, causing the blades to spin and accelerating the turbine. This process is highly efficient and, depending on the fuel used to heat the water, can be environmentally friendly.
Boilers are integral in numerous industries, such as railways, ships, thermal power plants, hotels, offices, and buildings. They find applications in various factories, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, textiles, paper mills, metal production, and sugar mills. Even in healthcare, boilers play a vital role.
These industrial systems are not only categorized by their applications but also by factors like portability, water circulation arrangement, position, output pressure valves, and the type of input fuel they use. Boilers are designed to be robust and reliable, ensuring that they can handle extreme pressure, making them indispensable in the modern industrial landscape.
In essence, an industrial boiler is a powerhouse of energy, driving industrial processes, electricity generation, and much more, making it a critical component in numerous sectors.
Types of Boiler and Classifications of Boiler:
There are following Boilers Types:
1. According to the position of water and hot gasses
2. According to Axis of Shell
- Horizontal Boiler
- Vertical Boiler
- Small Boiler
3. According to the position of the boiler
4. According to the pressure
5. According to the method of circulation
- Natural Circulation Boiler
- forced Circulation Boiler
6. According to use of boilers
- Mobile Boiler
- Stationary Boiler
7. According to drums
- Single drum Boiler
- Multi drum Boiler
8. According to the nature of drought
- Forced drought Boiler
- Natural drought Boiler
9. According to furnace
- Single furnace Boiler
- Dual furnace Boiler
10. According to fuel firing
- Solid fuel-fired Boiler
- Liquid fuel-fired Boiler
- Gaseous fuel-fired Boiler







Boiler Fuel Types
Boiler Furnaces compatible with following types of Fuels
Boiler Solid Fuels
- Wood fired boiler
- Coal fired boiler
- Briquettes fired boiler
- Pet Coke
- Rice Husk Fired boiler
Boiler Liquid Fuel
- LDO
- Furnace oil
Boiler Gaseous Fuels
- LPG
- LNG
- PNG can be used to carry out the combustion for a specific purpose.
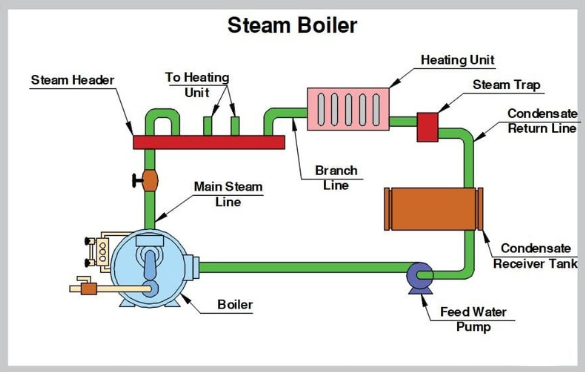
Components of a Boiler Systems
Boiler design is made up of 3 main components–
- Feed water system
- Steam system
- Fuel system
1. Boiler Feedwater System
Water that converts into steam by steam boilers system called Feedwater & system that regulates feed water called Feedwater system.
There are two types of feedwater systems in boilers:
- Open feed System
- Closed feed system
There are two main sources of feed water:
- Condensed steam returned from the processes
- Raw water arranged from outside the boilers plant processes ( Called: Makeup Water)
2. Boiler Steam System
Steam System is a kind of main controlling system of boilers process. Steam Systems are responsible to collect & control all generated steam in the process.
Steam systems send steam generated in the process to the point of use through pipes ( piping system). Throughout the process, steam pressure is controlled and regulated with the help of boilers system parts such as valves, steam pressure gauges, etc.
3. Boilers Fuel System
Fueling is the heart of boilers process & fuel system consists of all the necessary components and equipment to feed fuel to generate the required heat. The equipment required in the fuel system depends on the type of fuel used in the system.
Also Read: Packaged Boilers
Boiler Applications
The Boilers have a very wide application in different industries such as
- Power Sector
- Textiles
- Plywood
- Food Processing Industry
- FMCG
- Sugar Plants
- Thermal Power Plants
- knowledge pedia

Indian Boiler Manufacturer

Thermodyne design, manufacture and supply ISO 9001:2008 certified steam boilers, for such processes and several others too.
Thermodyne Engineering Systems can help you by saving up to 30% of the fuel cost by providing high-efficiency boilers, the Energy consultancy, and customized heating solutions.
Fuel-saving is not only important for margins, but also for the environment. The industry can count on Thermodyne because we believe in Enhancing Energy Efficiency.
Boiler Related Resources
- Boiler Losses That Eat Away Your Profits
- Dissolved Gases in Feed Water and Its Effect
- Pressure Reduction System
- How to minimize the Blowdown Losses
- Difference Between Dry Bottom and Wet Bottom Boiler
- What is a Combi Boiler
- Boiler Bag Filters
- Waste Heat Recovery Boiler ( WHRB Boilers)
- Deaerator Tanks Manufacturer
- Air Preheaters in Boiler – APH Types
- List of Thermal Power Plants in India
- Baby Boilers
Also, subscribe to our Youtube Chanel: Thermodyne Boilers
Boiler Working Explainer Video
Boiler Related Infographics

Boiler Application & Component Related FAQs
1. What is the Function of a Boiler?
A Steam Boiler is designed to supply dry and saturated steam at the required pressure, catering to high-volume demands. Its efficient operation ensures a consistent and abundant supply of steam, meeting the needs of various industries and applications.
2. What are the applications of Boilers?
There are several applications for boilers in industries –
1. In Operating steam engines.
2. In Operating steam turbines.
3. Industrial process work in chemical engineering.
4. For production, hot water needs to be supplied to rooms in extremely cold areas.
5. In thermal power stations
.
3. What are the sources of heat for the Boiler?
The source of heat for a boiler is obtained through the combustion of a wide range of fuels, including wood, coal, oil, rice husk, natural gas, and even nuclear fission. These fuel sources are utilized to generate the necessary heat energy for producing steam within the boiler system. The versatility in fuel option allows for flexibility in meeting specific energy requirements and enables the efficient operation of boilers in various industries.
4. How much does a new industrial boiler cost?
The cost of a new industrial boiler can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of boiler, its capacity, features, and the specifications required for your specific industrial processes. As a leading boiler manufacturer, Thermodyne Engineering System can provide you with a detailed and customized quote based on your needs.
Additionally, compliance with Indian Boilers Regulations is a crucial factor. Obtaining the necessary certification ensures that the boiler meets the required safety standards and regulations, which can impact the cost. The certification process involves rigorous inspections and adherence to specific guidelines, contributing to the overall expenses associated with acquiring a certified boiler
What is the average life of a Boiler?
The average life of a boiler can vary based on several factors, including the type of boiler, its design, maintenance practices, and operating conditions. Typically, well-maintained industrial boilers have a lifespan ranging from 20 to 30 years. However, this estimate is a generalization, and individual cases may differ.
How will you define boiler in layman’s terms?
Boiler Definition –
A boiler is an enclosed vessel that heats a liquid, such as water, to create steam or the vaporized form of a liquid. After that, the steam or hot water is circulated via a piping device to transport heat for a range of purposes, including heating, power generation, and other processes. Boilers and related systems are effective heat exchange systems, but if not properly managed and run, they can be unsafe. Improper management and operation of boilers can pose safety hazards.
What are the primary applications of steam boilers in hospitals?
Industrial Boilers used in Hospitals & Health Care for following applications –
-Operating room sterilization.
-Equipment sterilization.
-Production of clean steam.
-Providing heat for the building.
-Humidification for emergency rooms.
-Industrial laundry.
–Food preparation.
-Supplying steam for medical equipment sterilization.
-Generating clean steam for laboratory and research purposes.
-Providing heat for the entire facility, including patient rooms and administrative areas.
-Humidifying emergency rooms to maintain optimal conditions for patient care.
-Supporting industrial laundry operations for washing and sanitizing linens.
-Assisting in food preparation for hospital cafeterias and kitchens.
What is boiler definition in mechanical engineering?
As per mechanical engineering definition of boiler is” Boiler is a steam generator, which converts saturated water into steam by absorbing latent heat” In mechanical engineering, a boiler is considered a steam generator that converts saturated water into steam by absorbing latent heat. This process involves the transfer of energy from the water, causing it to undergo a phase change and transform into steam. The steam generated can then be utilized for various applications such as power generation, heating, or industrial processes that require high-temperature steam.
Boiler Losses That Eat Away Your Profits
The main goal for boiler operators is to conserve fuel and maximize heat energy utilization.
The conversion of fuel energy to thermal energy is not complete, resulting in various losses.
Losses can occur due to factors such as fuel moisture content, high stack gas temperatures, low material conductivity, and impurities in feed water.
These losses directly impact fuel consumption and increase operating costs.
Boiler operators need to be aware of these losses in order to optimize boiler operation.
A lack of knowledge about loss minimization and reduction can lead to ongoing financial losses for the industry.
What are the Industrial applications of a steam boiler?
Operating steam engines.
Operating steam turbines.
Operating reciprocating pumps.
Industrial process work in chemical engineering.
For producing hot water required to be supplied to rooms in very cold areas.
In thermal power stations
Dissolved Gases in Feed Water and Its Effect
In addition to other contaminants, natural water or raw water that is directly sourced from resources has various gases dissolved in it. These gases are produced by atmospheric air. In terms of boiler feed water, we are primarily concerned with oxygen and carbon dioxide, but other gases still make up a modest portion. These gases have an effect on the lifespan and operation of the boiler. Oxygen causes corrosion, which eventually causes the system to fail. It also lowers the quality of the steam, uses more fuel, reduces efficiency, and causes steam leakage. which is undesirable for a boiler operation that runs smoothly.
What are the different types of boilers?
There are many different types of boilers, but they can be broadly classified into two categories:
fire-tube boilers and water-tube boilers.
In a fire-tube boiler, the water is surrounded by tubes through which hot gases from the furnace flow. The steam generated collects above the water level in a cylindrically shaped drum.
In a water-tube boiler, the water flows through tubes that are surrounded by hot gases from the furnace. The steam generated is collected at the top of the boiler.
How do boilers work?
Boilers work by using heat to convert water into steam. The heat can come from a variety of sources, including burning fuel, electricity, or nuclear energy. Once the water is converted into steam, it can be used to generate power, heat buildings, or even cook food.
What are the benefits of using boilers?
Boilers offer a number of benefits, including:
They can be used to generate power, heat buildings, or cook food.
They are relatively efficient and can save energy costs.
They can be used in a variety of settings, including homes, businesses, and industrial facilities.
What are the safety considerations for using boilers?
Boilers can be dangerous if not properly used and maintained. Some of the safety considerations for using boilers include:
Boilers should be installed and operated by qualified professionals.
Boilers should be regularly inspected and maintained.
Boilers should be properly vented to prevent the buildup of hazardous gases.
Boilers should be kept away from flammable materials.
By following these safety considerations, you can help to prevent accidents and injuries.
What is the boiler definition as per IBR?
Definition of a boiler as per IBR (Indian Boilers Act):
Boiler: Any closed vessel exceeding 22.75 liters in capacity which is used expressly for generating steam under pressure and includes any mounting or other fitting attached to such vessel, which is wholly or partly under pressure when steam is shut off.
IBR also defines a number of other terms related to boilers, such as:
Design pressure: The maximum pressure that a boiler is designed to withstand.
Working pressure: The maximum pressure that a boiler is allowed to operate at.
Superheater: A device that increases the temperature of steam above its boiling point.
Economizer: A device that recovers heat from flue gases and uses it to preheat water entering the boiler.
Air preheater: A device that heats air before it enters the combustion chamber, which improves the efficiency of the boiler.
IBR regulations are designed to ensure the safety of boilers and to prevent accidents. Boiler owners and operators are required to comply with these regulations in order to operate their boilers safely.
Here are some of the key requirements of IBR:
Boilers must be designed, constructed, and installed in accordance with IBR standards.
Boilers must be operated by qualified personnel.
Boilers must be regularly inspected and maintained.
Boilers must be equipped with safety devices, such as pressure relief valves and safety valves.
By complying with IBR regulations, boiler owners and operators can help to prevent accidents and keep their employees and the public safe.
What is the average cost of a boiler?
The average cost of a boiler replacement in the United States is Rs 67,938. However, the cost can range from 74,290 to 110,070, depending on the type of boiler, the size of the boiler, and the location of the installation.
What is boiler ?
A boiler is a closed vessel that heats a liquid, such as water, to create steam or the vaporized form of a liquid. The steam or hot water is then circulated via a piping device to transport heat for a range of purposes, including heating, power generation, and other processes.